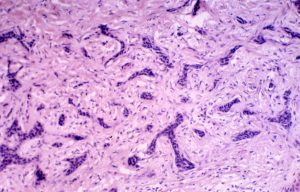
The human immune system is based on the formation of protective cells, leukocytes. A change in the white hematopoietic germ is accompanied by the pathology of these protective cells, and often leads to the development of a disease such as lymphogranulomatosis.
Lymphogranulomatosis, or Hodgkin’s disease, is a tumor of the circulatory system that changes normal white blood cells into abnormal cells. Hodgkin’s disease ranks second in frequency of occurrence among hematopoietic tissue tumors, second only to leukemia. A reliable cause of the disease has not yet been found, but there is a basic theory according to which lymphogranulomatosis occurs due to the action of the Epstein-Bar virus. Two age groups of the population are particularly susceptible to the disease: young people between the ages of 20 and 30 and those over 55.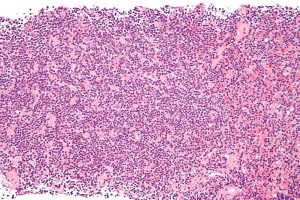
The clinical picture of lymphogranulomatosis
The disease occurs suddenly. A completely healthy person has unexpectedly enlarged lymph nodes. These can be groups of cervical, groin or axillary nodes. Such a symptom for no apparent objective reason usually makes the patient see a specialist. Sometimes patients are worried about shortness of breath, dry cough and swallowing problems. Such symptoms may be associated with the proliferation of lymphoid tissue inside the chest, which leads to compression of the organs located in it. In some cases, nonspecific complaints such as fever, chills, night sweats and sudden weight loss occur. On examination, the superficial lymph nodes are dense, not soldered to the surrounding tissue, and mobile. In about 35% of cases, patients complain of heaviness in the left hypochondrium. This is due to the enlargement of the spleen, characteristic of lymphogranulomatosis. As a result of damage to the immune system, the body’s defense against aggressive external factors weakens. It is possible to attach a bacterial and viral infection that worsen the patient’s condition.
Complex therapy
Lymphogranulomatosis is a disease, the treatment of which is more effective with a combination of different techniques. Thanks to modern methods of therapy, it is possible to achieve a stable remission in 75% of cases.
To influence the tumor are used:
Radiation therapy is the main, effective method of treatment. Due to the systemic exposure to radiation, not a single pathological cell remains protected. However, the problem is that healthy cells in the body also become defenseless. By destroying cancer cells, normal cells necessary for full-fledged life also die. This does not go unnoticed and leaves a lot of side effects. Multiple lesions of organs and tissues are manifested by a violation of their functions. Systemic manifestations are nausea, vomiting, headaches, and decreased performance.
Chemotherapy is a similar treatment. Aggressive action directed at tumor cells affects healthy ones along with them.
Photodynamic therapy https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photodynamic_therapy is a new method of treatment based on the use of photosensitizers. These drugs have the ability to accumulate in atypical cells without being absorbed by healthy cells. Under the action of a specialized light source, the photosensitizer inside the tumor cell begins to degrade, thereby affecting the tumor itself. Thus, it is possible to act on the tumor without harming the entire body. The solution to the problem is possible in a gentle, gentle way.