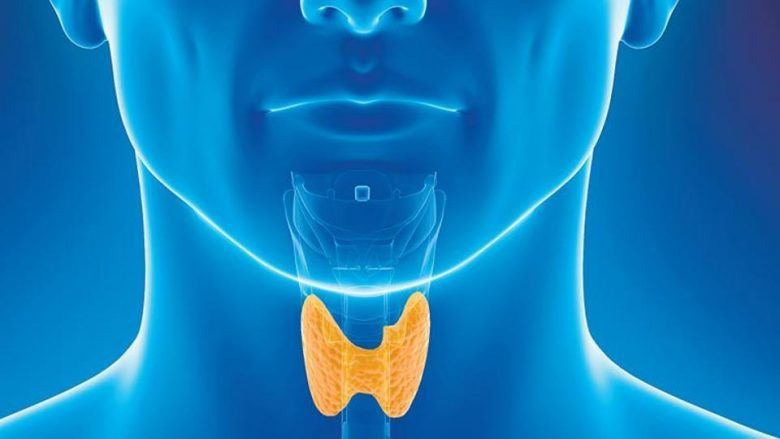
Situated on the front of the neck, this small butterfly-like organ determines the functioning of the entire body. The thyroid gland is the main regulator of the basal metabolism. Therefore, even healthy people, once every 2-3 years, it is useful to check how this organ functions. Well, for those who already suffer from one of the thyroid diseases, it is necessary to be examined at least once a year.
How common are thyroid problems?
Diseases of the thyroid gland are among the most common in the modern world. And among endocrine pathologies in terms of frequency of occurrence, they are in second place after diabetes mellitus. And every year the number of patients with these pathologies is increasing. So, in just 3 years, from 2013 to 2016, the incidence increased by 12%.
The most common thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism (lack and excess of hormones), Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Basedow’s disease (autoimmune pathologies). In recent years, the number of oncological diseases of the thyroid gland has been growing.
I am only 34 years old, but recently I got a feeling of a lump in my throat, as if a tie was tied tightly. I don’t notice bulging eyes (Graves’ disease). Could it be the thyroid gland?
People of any age are at risk of developing thyroid problems: from newborns to the elderly. But the most vulnerable categories are adolescents during puberty, pregnant women and women who have recently given birth, as well as women on the eve of menopause. They have hypothyroidism most often. In mature and elderly people, thyroid diseases are more often autoimmune in nature.
To control the condition of this most important organ and prevent dangerous complications, it is important to carry out timely diagnostics. The need for regular examinations of the thyroid gland is dictated by the fact that there are no specific symptoms that could accurately indicate its problems. Therefore, the diagnosis should not be based on the presence or those or other symptoms.
For example, a feeling of a lump in the throat or tight collar syndrome is thought to be a sure sign of nodular goiter. But in fact, this is not at all necessary, and such sensations may be associated simply with increased anxiety. But it still does not hurt to get checked.
However, the absence of any symptoms should not calm you down. For example, with Basedow’s disease, half of the patients develop bulging eyes, an unhealthy shine of the eyes and lacrimation, while the other half have none of this.
The possible symptoms of hypo- and hyperthyroidism are also not unambiguous. So, rapid weight gain, increased fatigue, apathy and memory impairment, which are often associated with a lack of iodine, can be caused, for example, by chronic fatigue syndrome, depression or vitamin D deficiency. A symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism (weight loss, heart palpitations, increased moisture of the skin), can occur with a mass of other pathologies (in particular, oncological). Therefore, in no case should one self-medicate and independently prescribe iodine preparations or some other medicines and folk remedies for preventive purposes. First you need to make a diagnosis.
I am going to sign up for a consultation with an endocrinologist about the thyroid gland. What tests do you need to go to the appointment with?
It is better to come to an endocrinologist already with research. Among the mandatory are thyroid ultrasound and hormone tests. Ultrasound will help identify pathologies such as endemic goiter, thyroiditis (inflammation of the gland), hypothyroidism, nodules, benign or malignant neoplasms. Hormone tests help to assess the function of the thyroid gland:
TSH – thyroid stimulating hormone,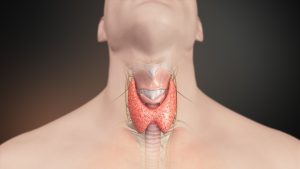
Free T4 (thyroxine).
It is very important to take tests in a complex, it is possible to correctly assess the change in the level of hormones only by comparing these two indicators.
But for a deep diagnosis of thyroid problems, these tests alone are not enough. The best option for examination is a laboratory complex:
Examination of the thyroid gland, screening, including the following tests:
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormone
Free thyroxine (free T4)
Free triiodothyronine (free T3)
Antibodies to thyroglobulin (Anti-TG)
Antibodies to microsomal thyroid peroxidase (Anti-TPO)
It is important to pay attention to antibodies to microsomal thyroperoxidase and thyroglobulin (anti-TPO and anti-TG). Antibody levels above normal can indicate an autoimmune process (for example, this happens with autoimmune thyroiditis).
It is important to do such an examination every year for people of any age to assess the function of the thyroid gland. In addition, it will be necessary to monitor treatment in the treatment of thyroid diseases. Such screening is especially important during pregnancy, since the course of pregnancy, as well as the physical and mental development of the fetus, depends on the function of the thyroid gland. Remember that the interpretation of the results can only be correctly carried out by the attending physician.