It is believed that there are safe doses of alcohol and on the Internet you can find norms that seem to be recommended by the world health organization. In fact, the WHO warns that there is no safe dose of alcohol.
We know that there is a level of alcohol consumption at which the risk of various ailments is low, but the WHO does not establish clear values for such doses, medical evidence suggests that it is safer for health not to drink. The more a person drinks, the higher the risk of getting sick. Alcoholic liver disease, which leads to cirrhosis, can become one of the serious, but quietly developing liver diseases.
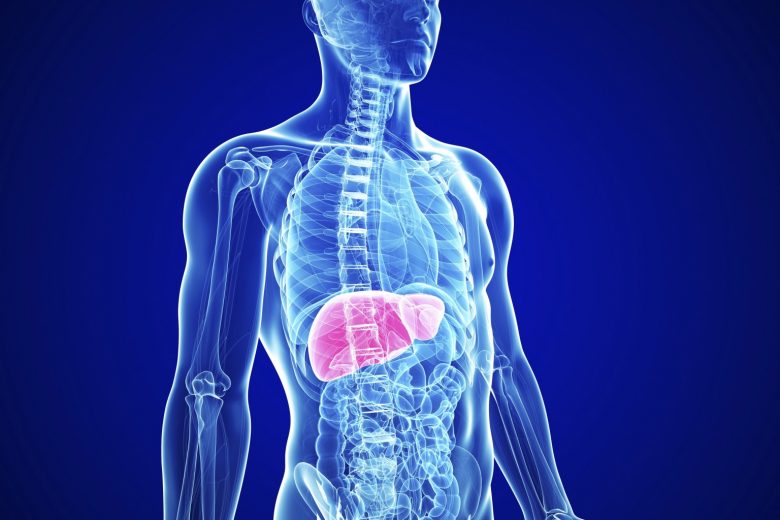
Often, a person simply does not know about problems with the liver, since this organ is very patient – and until it suffers thoroughly, it tries not to betray the existing problems in any way. Therefore, it is better to periodically check the condition of the liver.
Will the liver hurt if you exceed the safe alcohol intake?
Since there are no nerve endings in the liver, it is “silent” for a long time. Unpleasant sensations of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, pain and discomfort may appear due to stretching of the liver capsule when its size increases. As for jaundice, pruritus, dark urine and light stool, these symptoms can be signs of hepatitis – damage and inflammation of liver cells of infectious or toxic origin. A more common symptom of liver disease is loss of strength and increased fatigue, but since this symptom can be found in many other diseases. If painful symptoms bother, then you need to be examined. It is especially important to do this for those who do not adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle or have to take medications for a long time.
How to Watch Out for Liver Disease? What tests should be taken regularly?
The best thing we can do for our liver is, without expecting symptoms, to regularly take a biochemical blood test from a vein once a year, checking the level of bilirubin (direct and total) and 4 liver enzymes (AST, ALT, thyroid thyroid hormone and GGT) … This test – Examination of the liver, basic – will assess the toxic effect of harmful substances on the cells of the organ. This examination is necessary if you suspect a current liver disease or in conditions associated with both damage to the liver cells themselves, and with impaired outflow of bile.
Extended complex Liver examination is most appropriate for patients with pre-existing liver diseases both to assess the current state and to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. In addition to the above-mentioned analyzes, this complex includes a test for prothrombin, the level of total protein and protein fractions is determined, and the ability of the liver to synthesize the substances necessary for the body – cholinesterase and cholesterol, is assessed.
There are many different tests for liver disease. What is the most accurate analysis?
Blood tests for total, direct and indirect bilirubin are important markers for assessing liver function. They are usually prescribed when jaundice occurs or if liver disease (such as hepatitis) is suspected.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is an enzyme in the liver cells. When liver cells are damaged, the level of ALT in the blood rises. Moreover, this happens long before the onset of jaundice. A significant (more than 10-fold) increase in ALT levels is usually associated with either acute viral hepatitis or acute toxic liver damage. A moderate increase in ALT (several times) is characteristic of chronic viral hepatitis, impaired outflow of bile and chronic diseases of the hepato-biliary
zone, as well as alcohol abuse and liver damage in infectious diseases.
The second enzyme, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), is less indicative, but important in the complex diagnosis of liver function. It is usually given along with an ALT test.
An increase in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) can be observed in violation of the outflow of bile and other liver diseases, as well as in any form of cholestasis (difficulty in bile secretion).
GGT (gamma glutamyl transferase) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-glutamyltransferase is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of amino acids. Its increased concentration in blood serum is most often a marker of difficulty in the outflow of bile, as well as intoxication caused by alcohol or drugs. A blood test for GGT is important for the diagnosis of many liver diseases.
Why is there not one test, to assess liver function they always offer to pass a set of tests?
In fact, it is very important to pass all the tests in combination, because it is important to change each of the indicators in combination with each other. For example, high AST levels may indicate not only liver problems, but also damage to the heart muscle. Or, say, a simultaneous increase in GGT and ALP suggests cholestasis, but if GGT rises in isolation from ALP, then one can suspect that the whole point is in the long-term use of alcohol. An increase in alkaline phosphatase at normal GGT values rather speaks not of liver disease, but of the presence of bone tissue diseases.